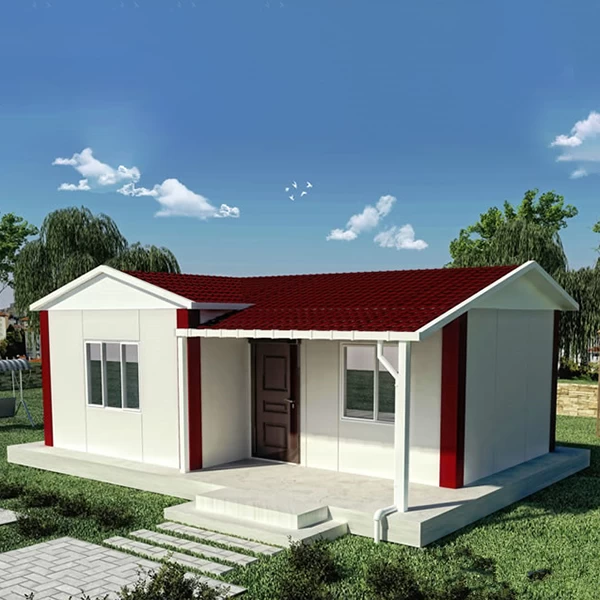
LIGHT STEEL INTEGRATED HOUSE---"FOUNDATION" (2)
Light steel integrated house---"Foundation" (2)
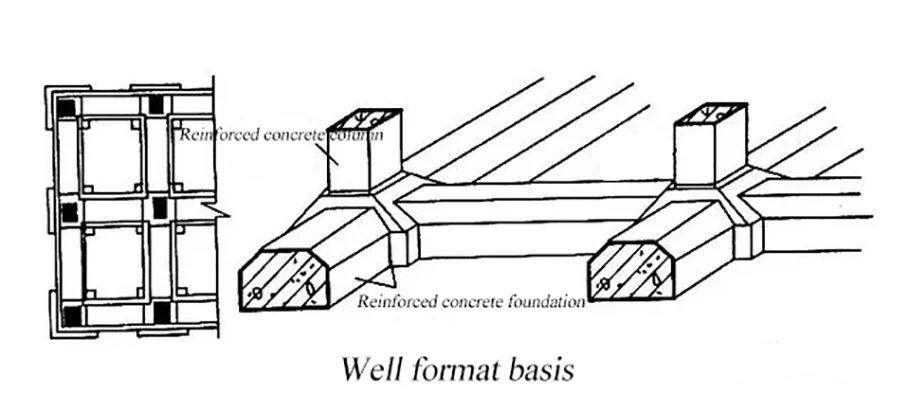
Well format basis
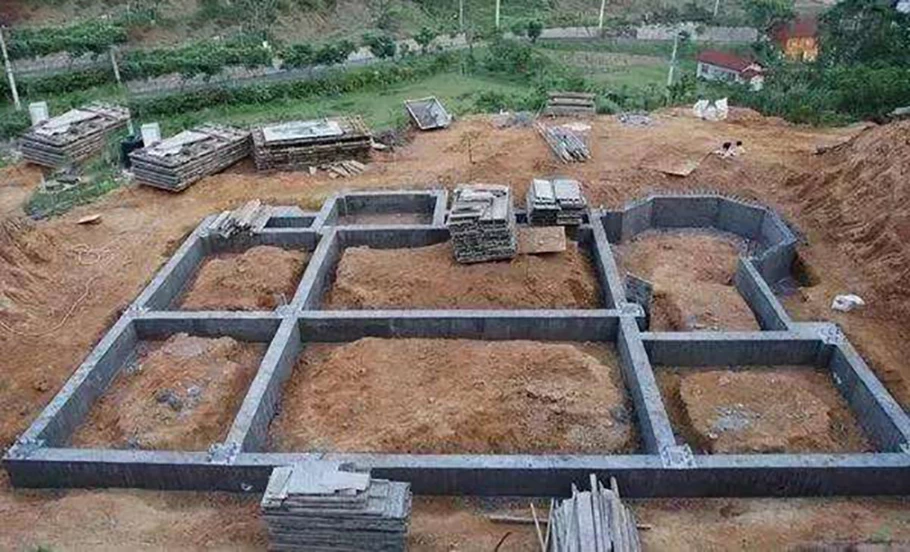

When the frame structure is in poor foundation condition or the upper load is large,
in order to improve the integrity of the building and prevent uneven settlement between the columns,
the foundation under the column is often extended and connected in two directions,
making a cross. The foundation of the well.
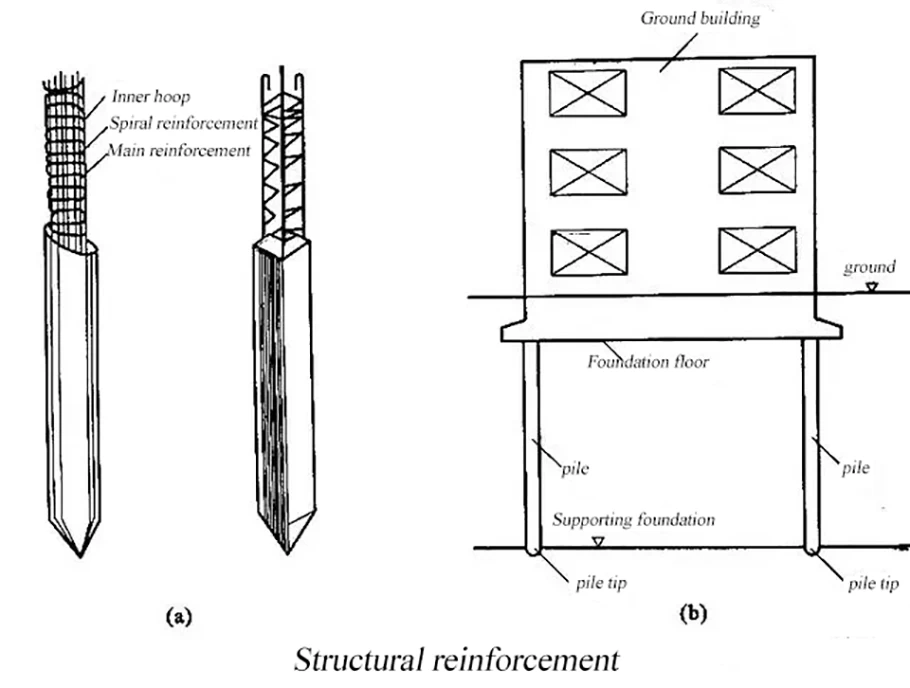
Pile foundation

The pile foundation consists of a pile and a platform connected to the top of the pile.
If the pile body is completely buried in the soil,
the bottom surface of the pile cap is in contact with the soil body,
which is called the low pile pile foundation;
if the pile body is exposed on the ground and the bottom of the pile platform is above the ground,
it is called the high pile pile foundation.

Features:
1. The pile is a vertical or slightly inclined foundation member with a cross-sectional dimension
that is much smaller than the length.
2. The piles placed in the geotechnical soil transfer the load of the superstructure to the foundation
through the lateral frictional resistance of the pile and the resistance of the pile end,
or transmit the lateral load to the lateral soil through the pile body.
Scope of application:
Widely used in high-rise buildings, bridges, high-speed rail and other projects.

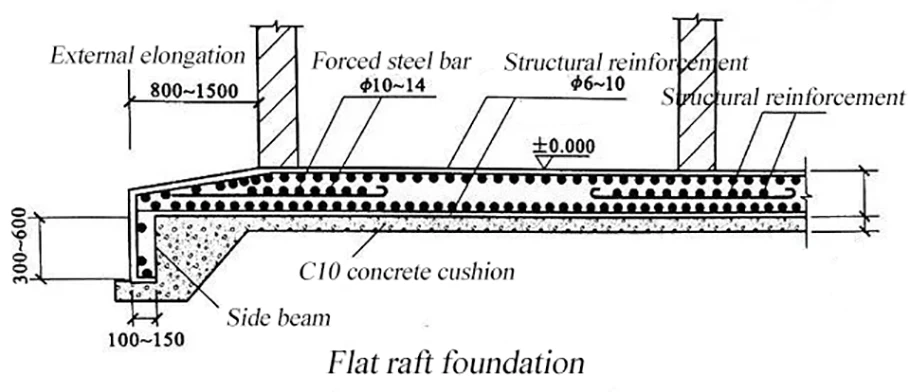
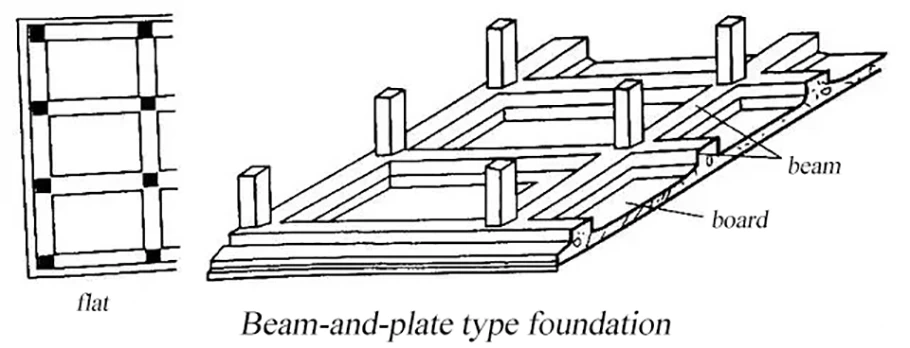
Raft foundation
Raft foundation, named full foundation.
It is to connect the independent foundation or the strip foundation under the column with the contact beam,
and then the bottom plate is integrally cast. It consists of a base plate, a beam, and the like.

Features:
Good overall, it can resist uneven settlement of buildings.
Scope of application:
The building has a large load and the bearing capacity of the foundation is weak.
The slab is often used to withstand the load of the building and form a raft foundation.

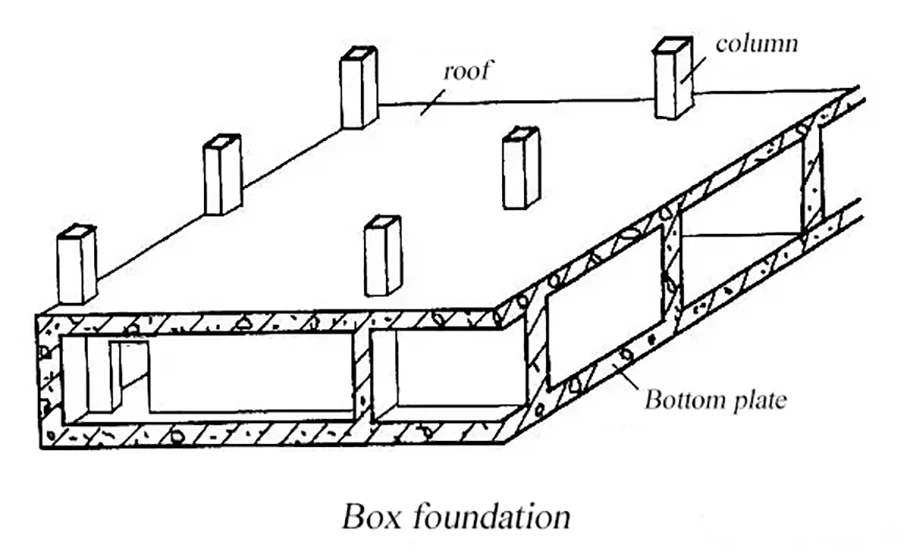
Box foundation
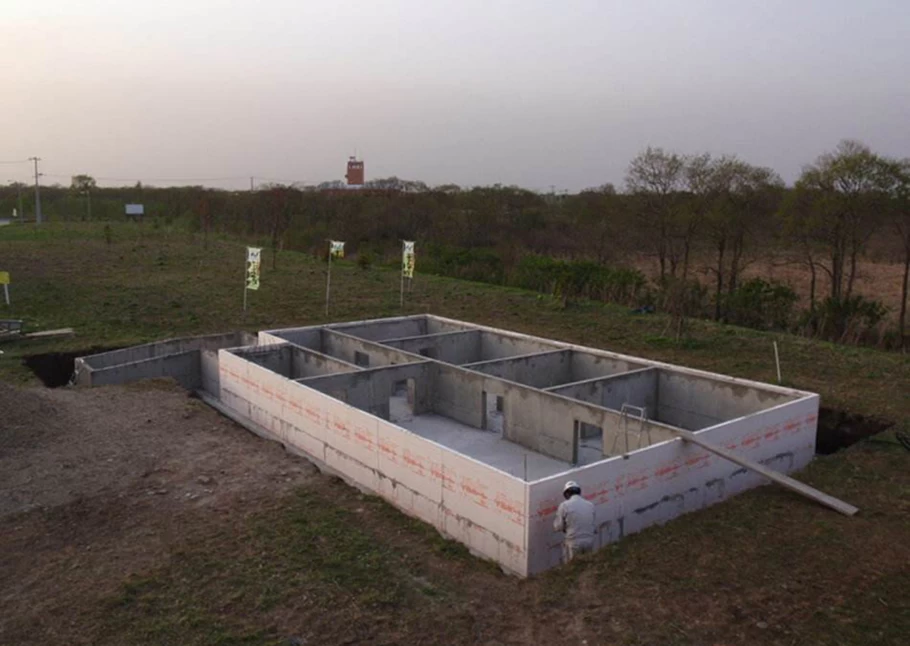

The box foundation refers to the overall cast-in-place reinforced
concrete structure composed of the bottom plate,
the top plate and the reinforced concrete longitudinal and transverse partition walls.

Features:
1. The box foundation has a large foundation bottom, a deep depth of embedding and a hollow structure.
Part of the load on the upper structure can be compensated for by the weight of the soil removed by excavation.
2. Compared with the general physical basis, it can significantly improve the stability of the foundation
and reduce the amount of foundation settlement.








-Heya-Low-Price-Prefab-Villa-Prefabricated-Steel-Structure-Villa-Made-In-China.jpg.webp)

